RBI Bulletin (March 2025): Navigating the Trade Deficit, Exports, and Economic Shifts
In an era marked by escalating global trade tensions and persistent geopolitical uncertainties, the Indian economy has demonstrated remarkable resilience and robust growth. The above findings are from Reserve Bank of India’s March 2025 bulletin which highlights the state of the economy in the country. The latest data-driven analysis underscores the strength of domestic fundamentals amidst a volatile global backdrop. While global economic uncertainties persist, India's economy shows strong growth, supported by robust consumption and government spending. Inflation has moderated, and policy measures have helped stabilize market liquidity. However, foreign portfolio outflows and currency depreciation remain key risks.
Domestic Economic Developments
Resilient GDP Growth Amidst Global Challenges
- India’s GDP is projected to grow by 6.5% in FY 2024-25, according to NSO’s Second Advance Estimates.
- Quarter 3 GDP growth was 6.2%, rebounding from 5.6% in Q2 due to higher private consumption and government spending.
- Sectors driving growth: construction, trade, and financial services.
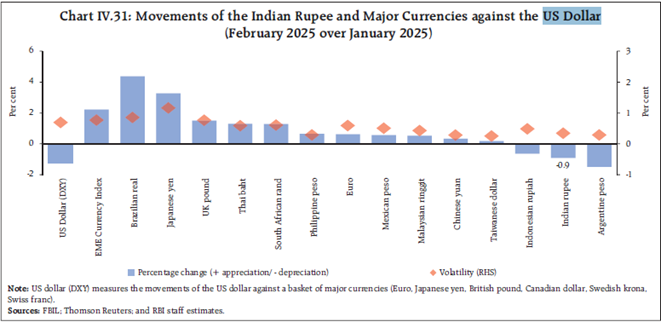
Foreign Portfolio Outflows & Currency Risks
- Sustained foreign portfolio investor (FPI) outflows put pressure on stock markets and the rupee.
- However, domestic investors increased their holdings, stabilizing market ownership structures.
- Rupee depreciation risks remain due to external uncertainties.
Inflation Trends: Headline Inflation Eases
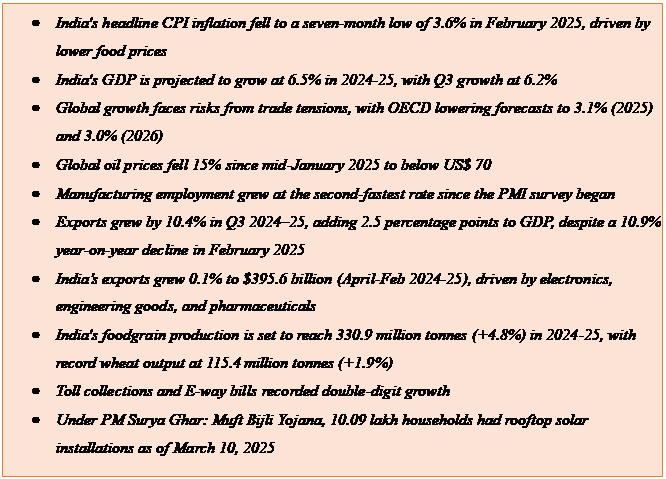
- CPI inflation fell to a 7-month low of 3.6% in February 2025, mainly due to a decline in vegetable prices.
- However, core inflation (excluding food & fuel) rose to 4.1%, indicating persistent price pressures.
Employment Trends
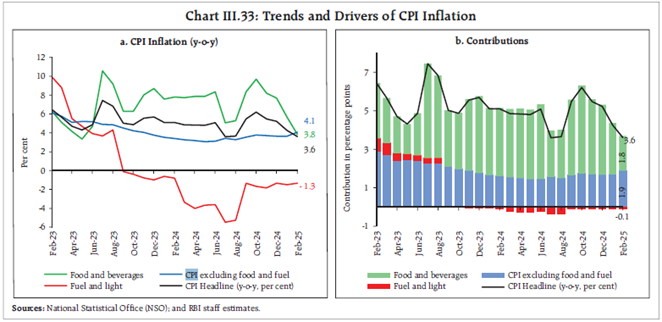
- Manufacturing employment grew at the second-fastest rate since the PMI survey began.
- Services sector employment also expanded significantly, reflecting strong demand.
- Urban unemployment remains at a historic low of 6.4%.
Trade & External Sector
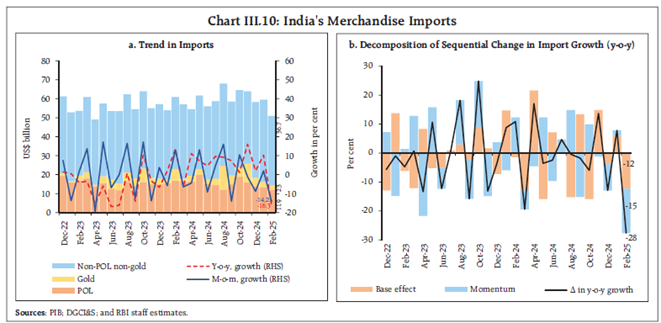
Import and Export Trends
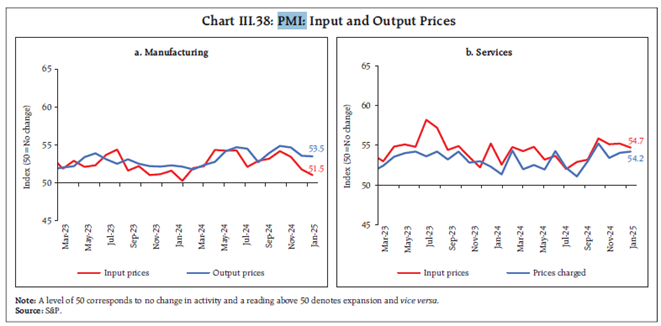
- Exports grew marginally by 0.1% to $395.6 billion from April 2024-Feb 2025 but merchandise exports declined by 10.9% YoY in February, largely due to base effects and weak global demand.
- Top-performing export sectors: electronics, rice, and ores.
- Weak export sectors: petroleum products, engineering goods, chemicals, and gems & jewellery.
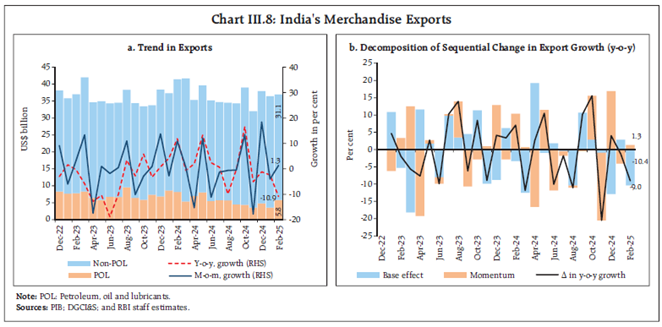
- Imports increased by 5.7% to $656.7 billion, driven by gold, electronics, and petroleum during April 2024-Feb 2025, however it fell by 16.3% in Feb 2025, leading to a narrowing trade deficit.
- Oil and gold imports dropped significantly, contributing to the decline in overall imports.
- Imports of electronic goods and machinery remained strong, reflecting domestic investment demand.
Financial & Monetary Policies
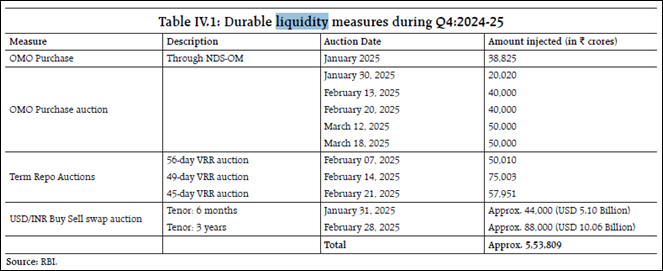
RBI’s Liquidity Management
- RBI used open market operations (OMO), daily repo auctions, and dollar/rupee swaps to manage liquidity.
- These measures helped stabilize domestic liquidity despite capital outflows.
Sector-Specific Developments
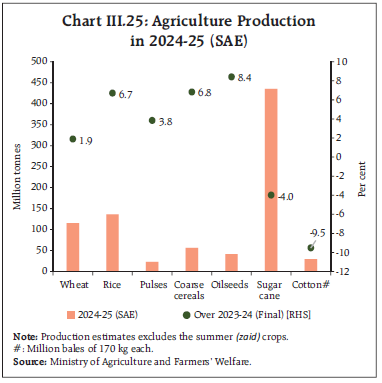
Agriculture Sector
India’s foodgrain production for 2024-25 is estimated at 330.9 million tonnes, marking a 4.8% increase from 2023-24, driven by kharif production up 6.8% and rabi up 2.8%, according to second advance estimates.
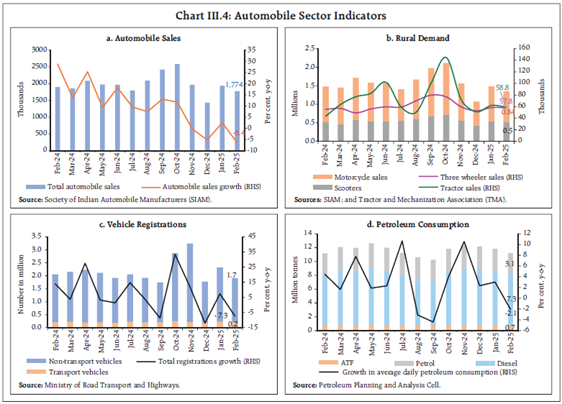
Automobile Sector
- Car and motorcycle sales declined in February due to weaker demand.
- Tractor sales saw double-digit growth, indicating strong rural economy demand.
Infrastructure & Construction
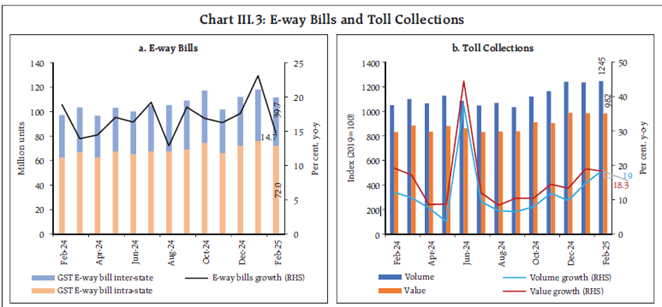
- Toll collections and E-way bills recorded double-digit growth, signalling robust infrastructure activity.
- Government spending on infrastructure projects supported economic momentum.
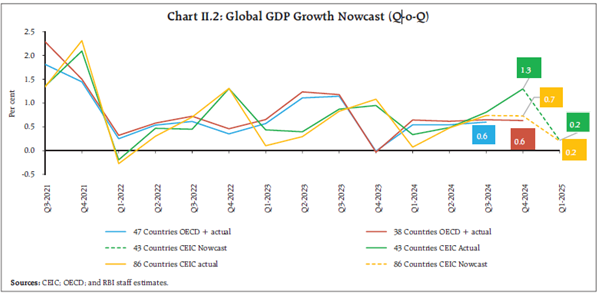
Global Setting
Trade War & Tariffs Impacting Growth
- The global economy entered 2025 with strong momentum but is now slowing due to increased protectionism and trade restrictions.
- US-China tariff escalations could reduce US GDP growth by 0.6 percentage points in 2025 and shrink the economy by 0.3-0.4% in the long run.
- OECD lowered global GDP forecasts to 3.1% in 2025 and 3.0% in 2026 due to slowing demand.
Market Volatility & Currency Fluctuations
- US dollar lost gains made since November 2024 due to trade policy uncertainty.
- European bond yields surged as Germany and others increased military spending.
- Equity markets worldwide have been volatile, reflecting fears of slowing growth.
Commodity Markets & Inflationary Pressures
- Global oil prices fell 15% since mid-January 2025 due to reduced demand expectations.
- Gold prices hit a record high of $3000 per ounce due to investor flight to safety.
- Food production outlook improved, with cereal production exceeding 2024 levels.
Conclusion
Despite global economic headwinds, India’s growth remains stable at 6.5%, supported by strong domestic demand. Inflation is under control, though core inflation remains sticky, necessitating careful monetary management. Trade challenges persist due to weak global demand, but a narrowing trade deficit offers some relief. While foreign investor outflows pose risks, robust domestic investment provides resilience. The RBI’s proactive policies have played a crucial role in stabilizing liquidity and inflation expectations. Overall, India’s economy is well-positioned for growth, but uncertainties in global markets, financial volatility, and trade disruptions remain key risks. Sustained policy support and domestic resilience will be essential in maintaining economic momentum.
References:
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/Bulletin/PDFs/0BULT19032025F9CCA0AB1F7294130A950E2FD5448B5FC.PDF
 9911796707
9911796707











