| News | |||
|
|
|||
GOVT CAPITAL EXPENDITURE ON KEY INFRA SECTORS GROWS AT 38.8 PERCENT BETWEEN FY 20 AND FY 25: ECONOMIC SURVEY 2024-25 |
|||
| 31-1-2025 | |||
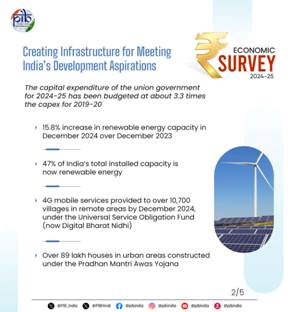
POWER SECTOR EXPANDS WITH INSTALLED CAPACITY RISING BY 7.2 PERCENT (YoY) TO 456.7 GW The Union Government‘s capital expenditure on key infrastructure sectors has grown at a rate of 38.8 per cent from 2019-20 to 2023-24. In 2024-25, Capital expenditure picked up momentum between July and November 2024. This was stated in the Economic Survey 2024-25 which was tabled by Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, in the Parliament today.
The power sector network continues to expand, with installed capacity rising by 7.2 per cent year-on-year to 456.7 GW as of November 2024. The addition of transformation capacity also gained momentum this year. In the shift towards renewable energy, the power sector has been bolstered primarily by large-scale solar and wind initiatives. By the end of December 2024, the country's total renewable energy installed capacity increased by 15.8 per cent year-on-year (YoY), reaching 209.4 GW, up from 180.8 GW in December 2023. With the implementation of the Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme, the daily average power supply has improved from 22.1 hours in FY14 to 23.4 hours in FY24 in the urban areas and from 12.5 hours in FY14 to 21.9 hours in the rural areas. The gap between energy demand and supply has also declined from 4.2 per cent in FY14 to a mere 0.1 per cent by December 2024.
Coming to the infrastructure in rural areas, the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) aims to ensure long-term water security for rural households by providing reliable access to safe piped drinking water. When it was launched in August 2019, only 3.23 crore (17 per cent) of rural households had tap water connections. Since then, over 12.06 crore families have been added, increasing the total to more than 15.30 crore (79.1 per cent) out of approximately 19.34 crore rural households as of November 26, 2024. Swachh Bharat Mission– Grameen (SBM-G) achieved open defecation-free (ODF) status in the first phase. Phase II of SBM-G is implemented from 2020-21 to 2024-25, with a focus on converting the villages from ODF to ODF Plus. Under Phase II of the Swachh Bharat Mission-Grameen, during April to November 2024, 1.92 lakh villages were incrementally declared ODF Plus under the model category, taking the total number of ODF Plus villages to 3.64 lakh. The impact of the Swachh Bharat Mission -Urban was felt. As per the 78th round report of NSS-15, it reports that 97 per cent of households in urban areas report access to toilets. As on December, 2024, the number of Individual household latrines constructed stands at 63.7 lakh, number of Community and public toilets constructed is 6.4 lakh and the number of wards with 100 percent door-to-door collection of municipal solid waste stands at 93,756. Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U), launched in 2015, aims to provide permanent housing in urban areas. As of November 25, 2024, a total of 1.18 crore houses have been sanctioned and over 89 lakhs completed. PMAY-U 2.0 was launched in September 2024 to assist an additional one crore households. Currently, 29 states and union territories have signed agreements to implement PMAY-U 2.0, with approval having been granted for 6 lakh houses in FY25. Metro rail and rapid rail transit systems are operational or under construction in 29 cities across India, with 1010 kilometres currently operational in 23 cities and an additional 980 kilometres underway. As of January 5, 2025, 62.7 kms were operationalised in FY25, and the daily ridership reached 10.2 million. These systems have led to considerable savings in emissions, time, vehicle operating costs, accidents and infrastructure maintenance. Under the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) which focused on improving urban water management in 500 cities, tap water coverage has increased to 70 per cent, and sewerage coverage has risen to 62 per cent. The mission has created or augmented water treatment capacity of 4,649 million litres per day and developed 2,439 parks, adding 5,070 acres of green space. In 2021, AMRUT 2.0 was introduced to expand coverage to all statutory towns and cities, with an allocation of ₹2.77 lakh crore during 2021-22 to 2025-26. This phase so far has initiated 8,923 projects worth ₹1.89 lakh crore. AMRUT 2.0 actively involves self-help groups and promotes innovative technologies. Under Smart City Mission, as on 13 January 2025, a total of 8,058 projects worth 1.64 lakh crore have been proposed, with 7,479 projects worth 1.50 lakh crore completed. Referring to the Real Estate development, the Survey has mentioned that the rules under the Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act, 2016 (RERA) have been notified in all States and Union Territories except Nagaland, with various regulatory authorities established. About 1.38 lakh real estate projects and 95,987 real estate agents have been registered under the Real Estate Regulatory Authority as of January 6, 2025. 1.38 lakh complaints have been disposed of by the RERA across the country. About the tourism infrastructure development, the Survey has stated that under Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual Augmentation Drive (PRASHAD) scheme, as of December 2024 a total of 48 projects were sanctioned and out of it a total of 26 projects have been completed. Under Swadesh Darshan, which is aimed at the integrated development of tourism destinations, including theme-based tourist circuits, a total of 76 projects were sanctioned and 75 of them have been completed. The Space infrastructure, the Survey notes that India currently operates 56 active space assets, including 19 communication satellites, nine navigation satellites, four scientific satellites, and 24 earth observation satellites. ISRO has enhanced its capabilities by adding a small satellite launch vehicle to its fleet. New Space India Limited (NSIL) successfully fulfilled its contract to launch 72 OneWeb satellites into low earth orbit. Recently it also launched the GSAT-20 satellite in collaboration with Space X.
The Survey concludes by saying that the strategy to step up private participation needs coordinated action of all stakeholders involved - governments at different tiers, financial market players, project management experts and planners, and the private sector. Capacities to conceptualise projects, develop sector-specific innovative strategies for execution, and, develop high-expertise areas such as risk and revenue sharing, contract management, conflict resolution and project closure need to improve substantially. The efforts of the Union Government would need to be supplemented with wholehearted acceptance of the need for public-private partnerships in infrastructure across the country. |
|||
 9911796707
9911796707