| News | |||
|
Home |
|||
|
|
|||
Ministry of Finance Year Ender 2023: Department of Economic Affairs |
|||
| 27-12-2023 | |||
The Year 2023 marks the beginning of ‘Amrit Kaal’ - the 25-year period beginning from the 75th anniversary of its independence on 15th August 2022, leading up to the centenary of its Independence, towards a futuristic, prosperous, inclusive and developed society, distinguished by a human-centric approach at its core. India continues to be one of the fastest-growing economies of the world. The country's second quarter growth, 7.6 per cent, has been then highest in the world and India's GDP growth for the April-June quarter was 7.8 per cent. Putting into effect the roadmap for making India a $5 trillion economy, the Government continues to focus on growth at the macro level and complementing it with all-inclusive welfare at the micro level, promoting digital economy and fintech, technology-enabled development, energy transition and climate action and relying on a virtuous cycle of investment and growth. The Government has also focused on a capex-led growth strategy to support economic growth and attract investment from the private sector, increasing its capital investment outlay substantially during the last three years. Central Government’s capital expenditure has increased from 2.15 per cent of GDP in 2020-21 to 2.7 per cent of GDP in 2022-23. To fuel such achievements, the Government has worked tirelessly for shouldering a number of bold and important socio-economic reforms. The Government has undertaken its reform drive with the spirit of inclusiveness of the marginalised and hitherto socio-economically neglected classes in the overall development process. The success of Government’s policies is further reaffirmed and underscored when the International Organisations like the World Bank and IMF recognise India as the fastest growing Emerging Market Economy (EME) in the world and applaud the resilient and stable growth India continues to witness. The Year 2023 is also significant as India hosted the G20 Presidency from December 1, 2022 to November 30, 2023. The 43 Heads of Delegations - the largest ever in G20 - participated in the final New Delhi Summit in September 2023. The G20 Finance Track under India's leadership addressed critical global issues, including the strengthening of Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs) through the G20 Independent Expert Group's comprehensive report. The DEA played a pivotal role in fostering cooperation on crypto-assets, with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the Financial Stability Board (FSB) developing a Synthesis Paper adopted as the G20 Roadmap on Crypto Assets in October 2023. During the G20 Indian Presidency, India steered the G20 agenda and hosted the Summit. The G20 consists of two parallel tracks: the Finance Track and the Sherpa Track. Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors lead the Finance Track, while Sherpas lead the Sherpa Track. The high point of the Leaders’ Summit was that a global consensus was arrived at in the form of New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration (NDLD). The department facilitated debt restructuring efforts through the Common Framework and launched the Global Sovereign Debt Roundtable, reinforcing its commitment to supporting vulnerable economies. Initiatives like the G20 Sustainable Finance Technical Assistance Action Plan (TAAP) underscored efforts to enhance capacity-building in sustainable finance, particularly for Emerging Markets and Developing Economies. Infrastructure development also received a boost through initiatives like the Harmonised Master List (HML) of Infrastructure Sub-sectors, the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), and the G20 Infrastructure Working Group's consensus on key deliverables. The DEA's strategic measures for promoting Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) include the VGF Scheme's expansion and the revamping of the Infrastructure Investment Project Development Fund (IIPDF). The DEA also played a role in financial sector reforms, including the launch of the NSE IFSC-SGX Connect and the transition to a T+1 settlement cycle, positioning India as a pioneer in global securities markets. In summary, the Department of Economic Affairs in 2023 has demonstrated a proactive and inclusive approach, contributing significantly to sustainable finance, climate action, infrastructure development, and financial sector reforms on both national and international fronts. Following are some of the major achievements of the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, in 2023: Sovereign Green Bonds: In the Union Budget 2022-23, the Government announced that, as a part of the government’s overall market borrowings in 2022-23, sovereign Green Bonds will be issued to mobilize resources for green infrastructure. The proceeds will be deployed in sector projects which help in reducing the carbon intensity of the economy.
In pursuance of the above budget announcement, framework for Sovereign Green Bonds has been brought out by the Government of India to mobilise resources for green infrastructure projects which help in reducing the carbon intensity of the economy. The Government has raised ₹16,000 crore, through issuance of Sovereign Green Bonds in 2023 till date and these proceeds were allocated to the eligible schemes/projects of the Ministries/Departments such as New and Renewable Energy, Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Housing and Urban Affairs, Railways etc. In the FY 2023-24, Government has decided to raise ₹ 20,000 crore through issuance of Sovereign Green Bonds. Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC): The introduction of the Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) reflects the government's dedication to women's financial inclusion. With total number of accounts opened are at 14,83,980 with deposit of Rs. 8,630 crore as on July 2023, this initiative empowers women economically, offering an attractive 7.5% interest rate compounded quarterly. Mahila Samman Savings Certificate (MSSC) was launched by the Government of India to commemorate the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav. MSSC account may be opened by women of any age group including the girl child with a minimum deposit of ₹1000/- and maximum deposit of ₹2 Lakhs for a period of two years. This scheme is available for a two-year period up to March 2025. The facility of partial withdrawal and premature closure on compassionate grounds are also available under this Scheme. Government of India has authorized Department of Posts, all Public Sector Banks and four Private Sector Banks to operate MSSC.
he maximum deposit for the senior citizen saving scheme has been enhanced from Rs 15 lakhs to Rs 30 lakhs. The maximum deposit limit for the Post office monthly Income savings scheme is enhanced from Rs.4.5 lakh to Rs.9 lakh for a single account and from Rs.9 lakh to Rs.15 lakh for a joint account. Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) The Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY) is a savings scheme initiated by the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, specifically designed for the benefit of the girl child. The scheme was launched as part of the ‘Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao’ campaign to promote the welfare of the girl child and encourage parents to save for their education and marriage expenses. So far, 3.2 crore accounts are active under the Scheme. National Investment and Infrastructure Fund in 202:
G20 Finance Track under India’s G20 Presidency, 2023:
KEY OUTCOMES OF THE G20 FINANCE TRACK IN 2023:
Report of the G20 Independent Expert Group on Strengthening Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs)
IMF-FSB Synthesis Paper on crypto-assets:
G20 Principles for Financing Cities of Tomorrow:
Mechanisms for timely and adequate mobilization of climate finance:
G20 Policy Recommendations for advancing financial inclusion and productivity gains through DPI and New Financial Inclusion Action Plan 2024-26:
Managing global debt vulnerabilities:
G20 Sustainable Finance Technical Assistance Action Plan (TAAP):
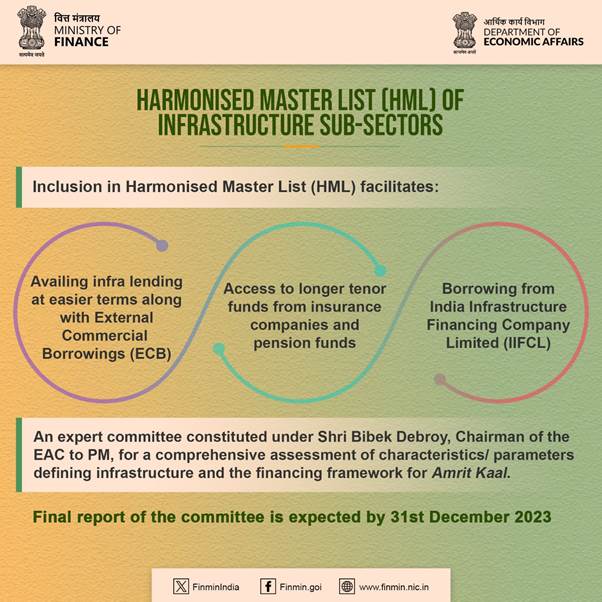
INITIATIVES TO BOOST INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTMENT (a) Harmonised Master List (HML) of Infrastructure Sub-sectors: As of now, HML list includes 37 Infrastructure sub sectors under 5 categories i.e., 1. Transport and Logistics, 2. Energy, 3. Water and Sanitation, 4. Communication and 5. Social and Commercial Infrastructure. The inclusion of any sector in the HML enables it to avail infrastructure lending at easier terms and External Commercial Borrowings (ECB), access to longer tenor funds from insurance companies and pension funds and be eligible to borrow from India Infrastructure Financing Company Limited (IIFCL) etc. In accordance with para 49 of the Union Budget for FY 23-24, an expert committee has been constituted under the chairmanship of Shri Bibek Debroy, Chairman of the EAC to PM with the objective to undertake a comprehensive assessment of the characteristics/ parameters defining infrastructure and the financing framework for Amrit Kaal. The Expert Committee had a series of stakeholder’s consultations and is finalising the recommendations and the final report of the committee is expected by 31st December 2023
(b) National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP): Infrastructure is one of the key enablers for economic growth. The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) comprises brownfield and greenfield infrastructure projects of above INR 100 Crores across both economic and social infrastructure sectors. The pipeline consists of projects implemented by all the States and Union Territories of India and 22 Infrastructure Ministries of Govt. of India. NIP was launched with 6,835 projects and has expanded to capture over 9,288 projects with a total project outlay of Rs 108.88 lakh cr between 2020-2025. Transport (42%), energy (25%), water & sanitation (15%) and social infrastructure (3%) sectors amount to around 85% of the projected infrastructure investments under NIP. NIP projects are housed on the India Investment Grid (IIG) portal (https://indiainvestmentgrid.gov.in/).
c. G20 Infrastructure Working Group: Infrastructure Working Group under the Indian G20 Presidency was able to bring a consensus amongst the members on four major deliverables namely i) the G20 Principles on Financing Cities of Tomorrow, ii) the G20/OECD Report on financing cities of tomorrow, iii) the G20/ADB Framework on Capacity Building of Urban Administrations, and iv) G20/WB Report on Enablers of Inclusive Cities. d. Regulatory reforms for infrastructure financing: SEBI amended the InvIT Regulations further in 2023 to introduce a range of corporate governance and audit related prescriptions for InvITs. This will make this investment avenue even more safe, qualitative, and attractive in the long term for different investor classes in and outside the country.
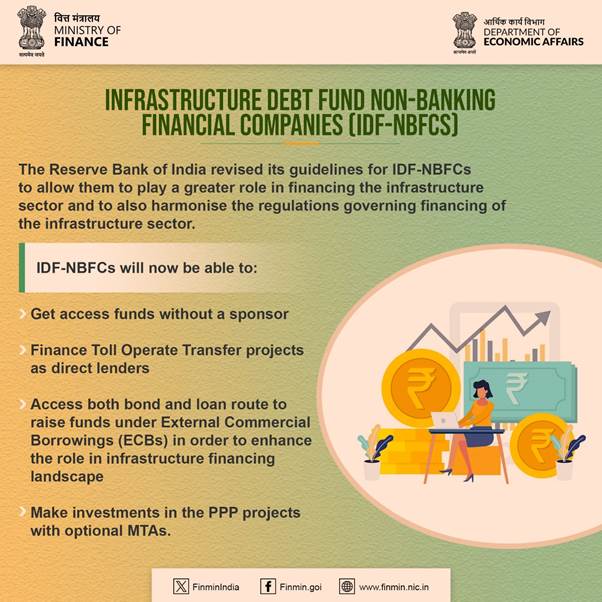
e. RBI has recently introduced updated guidelines for Infrastructure Debt FundNon-Banking Financial Companies (IDF-NBFCs) to enable them to access funds without a sponsor, finance Toll Operate Transfer projects as direct lenders and access external commercial borrowings in order to enhance the role of IDF-NBFCs in financing the infrastructure sector and to align the regulations governing infrastructure sector financing by Non- Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
Initiatives for Promoting PPPs: a. VGF Scheme: Under the existing VGF Scheme, it had been observed that majority of the projects taking benefit of the scheme were from economic sectors like roads etc. In order to promote PPPs in social sector like health, education etc., the ambit of the existing VGF Scheme was expanded and the scheme was revamped in 2020 to include higher VGF support of upto 80% of CAPEX and upto 50% of OPEX for PPPs depending on project sector and contours. During 2023, EC has accorded ‘In-principle’ approval for VoC Port Project in Tuticorin, GoTN with TPC of ₹7,055 Cr and GoI VGF share of ₹1,450 Cr. Further, during 2023, Rs.410 Cr. have been disbursed under the VGF Scheme. b. Revamping of IIPDF: The existing IIPDF was structured as a revolving fund with disbursement in the form of a refundable loan. Due to these stringent provisions, there was not even a single proposal being received under IIPDF in the past 3-4 years. In order to improve the uptake of the IIPDF, the existing fund was revamped and launched as a Central Sector Scheme on 03.11.2022 to provide support to PPP project authorities for undertaking PPP Project Preparation. During 2023, 16 projects from 11 States with TA cost of Rs.33.40 Cr. have been approved for funding under IIPDF Scheme and many more in the pipeline stage. c. Empanelment of TAs: A long standing demand from the Central and State PSAs had been for providing a list of pre-qualified Transaction Adviser and streamlining the process of onboarding of Transaction Advisers for undertaking quality PPP project structuring. Accordingly, 12 TAs have been empanelled by DEA through an RFQ process and panel has been notified on 01.07.2022. further a Manual for the utilisation of the panel has also been issued. The TA panel has seen good uptake among states and has been utilised for over 40 PPP transactions till date. d. Policy measures and Documents for supporting and mainstreaming PPP ecosystem such as – Reference Guide for Setting up State PPP units, Reference Guide for PPP project Appraisal and Reference Guide for Project Implementation Mode Selection-Waterfall Framework etc. were prepared and developed. e. IT Innovations - Revamping of the PPPININDIA website and Best Practices online portals for PPPAC, VGF, IIPDF was undertaken to streamline the application process. f. PPP Appraisal - As the Central Nodal authority for appraisal of PPPs, the PPPAC housed in the DEA appraised VOC Port PPP Projects with TPC of ₹7,056.00 Cr and Monetization of Telecom Tower Assets of BSNL under on Operate Maintain Transfer (OMT) Concession with TPC of Rs.4,200 Cr. Knowledge Dissemination and promoting Cooperative Federalism: During the period, a total of 3 Workshops were organised - Two State Outreach workshops, One workshop on ‘PPP Structuring Toolkit’. The workshops elicited good response and the impact was that the awareness of GoI schemes for promoting PPPs were disseminated and witnessed further traction. Financial Sector Reforms
T+1 Settlement: In January 2023, India, one of the earliest adopters of T+1 settlement system in the global securities market, well ahead of major developed and emerging markets. The clearing and settlement system of Indian securities market completed its transition to T+1 settlement cycle based on a phased implementation which was initiated in November 2021. So far, under the T+2 settlement cycle, trades on the Indian stock exchanges were settled within two working days. For instance, if an investor buys/sells shares on a T (Trade) day, then the settlement of the trade, i.e. pay-in and pay-out of securities and funds would be completed within two working days i.e. by T+2 day. Under the T+1 settlement cycle, the settlement of such trade will take place within one working day i.e. by T+1 day, resulting in faster delivery of securities. The switch to T+1 settlement cycle shall benefit investors by increasing market liquidity as the securities/funds of trades carried out on T day will be available on the next working day itself. An early settlement of funds/securities under a T+1 settlement cycle would also enable faster redemption for mutual funds, thereby benefiting the retail investors. In addition, T+1 settlement cycle include usher in a ecosystem of increased trading turnover and reduced settlement risk thereby leading to overall development of the securities market. India has become one of the very few large economies that switched from T+2 to T+1 settlement. The shorter settlement cycle (T+1) is in the interest of retail investor as it reduces the risk of non-payment or non-delivery of shares by the broker by one day, which is an improvement over the present system. Further, faster trade settlements lead to better efficiency levels and further protect investors.
|
|||
 9911796707
9911796707